| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
Tags
- zip 암호화
- aggregation
- Elasticsearch
- Test
- licence delete curl
- 파이썬
- Java
- 차트
- 900gle
- query
- sort
- Kafka
- analyzer test
- TensorFlow
- flask
- matplotlib
- license delete
- plugin
- high level client
- springboot
- API
- Python
- zip 파일 암호화
- aggs
- token filter test
- Mac
- ELASTIC
- License
- docker
- MySQL
Archives
- Today
- Total
개발잡부
선형회귀 본문
반응형


import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
param1 = random.randint(1,5) #기울기
param2 = random.randint(20,40) #편향
data = [[3,24], [6,48], [9,40], [12, 52]]
x = np.array([i[0] for i in data])
y = np.array([i[1] for i in data])
plt.plot(x,y,"b.")
def model(x):
y = param1 * x + param2
return y
def rmse(predict, true):
return np.sqrt(((predict - true) ** 2).mean())
predict = []
for i in x:
predict.append(model(i))
predict = np.array(predict)
plt.plot(x, predict, "r-")
plt.plot(x, y, "b.")
rmse_result = rmse(predict, y)
print(rmse_result)
for k in range(10):
param1 = random.randint(1,5)
param2 = random.randint(2,40)
predict = []
for i in x:
predict.append(model(i))
predict = np.array(predict)
rmse_result = rmse(predict, y)
print("Param1: {}".format(param1))
print("Param2: {}".format(param2))
print("RMSE: {}".format(rmse_result))
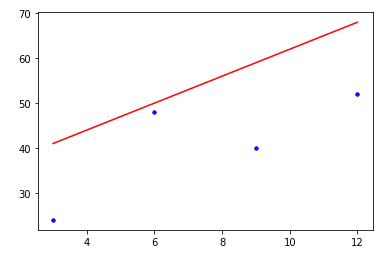
선형회귀란
- 종속변수 y와 한 개 이상의 독립변수 x와의 선형 상관 관계를 모델링하는 기법
- 최적의 기울기(weight)와 편향(bias)을 구하는 것이 문제
- 평가 기준을 세워 최적의 기울기와 편향을 탐색
- 단순 반복을 해서 최적의 파라미터를 찾는 것은 어렵다.
반응형
'강좌' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [cnn] Residual block (0) | 2022.08.07 |
|---|---|
| [tf] 11. RNN (0) | 2022.07.31 |
| [tf] 3. Convolution Layer (0) | 2022.07.31 |
| 12.Multi-Classification 실습 (0) | 2022.05.14 |
| google colab (0) | 2022.03.24 |
Comments




